Support Scheduler - Purpose
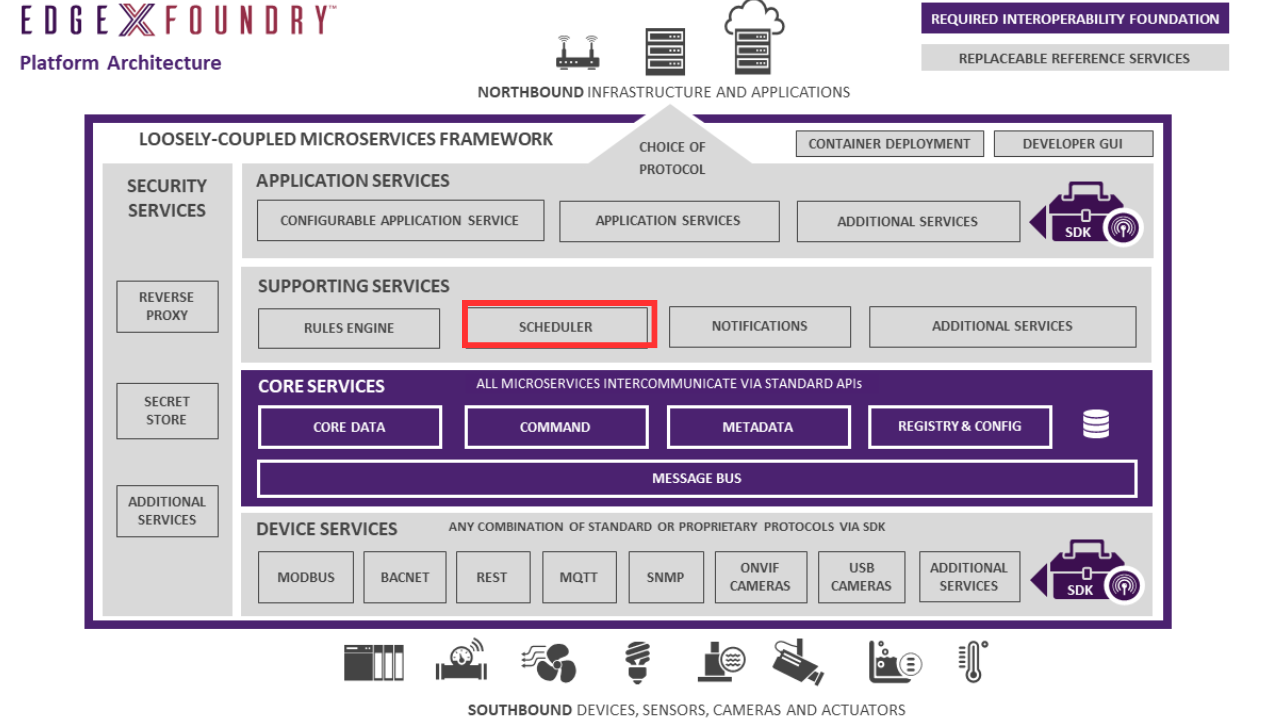
The support scheduler microservice provide an internal EdgeX “clock” that can kick off operations in any EdgeX service. At a configuration specified time (called an interval), the service calls on any EdgeX service API URL via REST to trigger an operation (called an interval action). For example, the scheduler service periodically calls on core data APIs to clean up old sensed events that have been successfully exported out of EdgeX.
Default Interval Actions
Scheduled interval actions configured by default with the reference implementation of the service include:
- Clean up of Core-data events/readings that have been persisted for an extended period. In order to prevent the edge node from running out of space, these old events/readings are removed. This is the "ScrubAged" operation. Scheduler parameters around this operation determine how often and where to call into Core-data to invoke this operation to expunge of old data.
Note
The removal of stale records occurs on a configurable schedule. By default, the default action above is invoked once a day at midnight.
Scheduler Persistence
Support scheduler uses a data store to persist the Interval(s) and IntervalAction(s). Persistence is accomplished by the Scheduler DB located in your current configured database for EdgeX.
Info
Redis DB is used by default to persist all scheduler service information to include intervals and interval actions.
ISO 8601 Standard
The times and frequencies defined in the scheduler service's intervals are specified using the international date/time standard - ISO 8601. So, for example, the start of an interval would be represented in YYYYMMDD'T'HHmmss format. 20180101T000000 represents January 1, 2018 at midnight. Frequencies are represented with ISO 8601 durations.