Cross Cutting Concerns
Event Tagging
In an edge solution, it is likely that several instances of EdgeX are all sending edge data into a central location (enterprise system, cloud provider, etc.)
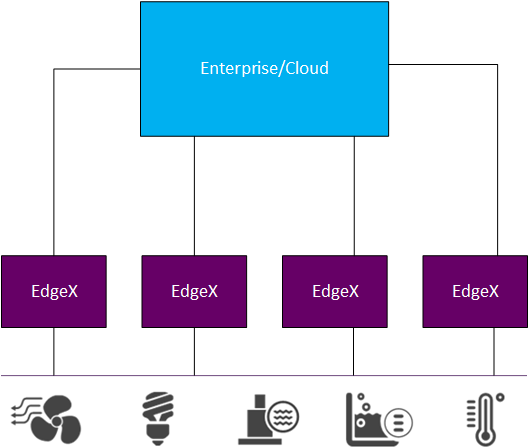
In these circumstances, it will be critical to associate the data to its origin. That origin could be specified by the GPS location of the sensor, the name or identification of the sensor, the name or identification of some edge gateway that originally collected the data, or many other means.
EdgeX provides the means to “tag” the event data from any point in the system. The Event object has a Tags property which is a key/value pair map that allows any service that creates or otherwise handles events to add custom information to the Event in order to help identify its origin or otherwise label it before it is sent to the north side.
For example, a device service could populate the Tags property with latitude and longitude key/value pairs of the physical location of the sensor when the Event is created to send sensed information to Core Data.
Application Service Configurable
When the Event gets to the Application Service Configurable, for example, the service has an optional function (defined by Writable.Pipeline.Functions.AddTags in configuration) that will add additional key/value pair to the Event Tags. The key and value for the additional tag are provided in configuration (as shown by the example below). Multiple tags can be provide separated by commas.
[Writable.Pipeline.Functions.AddTags]
[Writable.Pipeline.Functions.AddTags.Parameters]
tags = "GatewayId:HoustonStore000123,Latitude:29.630771,Longitude:-95.377603"
Custom Application Service
In the case, of a custom application service, an AddTags function can be used to add a collection of specified tags to the Event's Tags collection (see Built in Transforms/Functions)
If the Event already has Tags when it arrives at the application service, then configured tags will be added to the Tags map. If the configured tags have the same key as an existing key in the Tags map, then the configured key/value will override what is already in the Event Tags map.
Service Metrics
Edgex 2.2
New for Edgex 2.2
Note
Service metrics are Beta released for EdgeX 2.2. Breaking changes, while not likely, may occur as more use of service metrics are added.
Limited service metrics have been added for the EdgeX 2.2 release. Currently, only Core Data and Application Services are collecting a limit set of service metrics. Additional service metrics will be added to Core Data, Application Services and other services in future releases. See Writable.Telemetry at Common Configuration for details on configuring the reporting of service metrics.
See Custom Application Service Metrics for more detail on Application Services capability to collect their own custom service metrics via use of the App SDK API.
Each service defines (in code) a set of service metrics that it collects and optionally reports if configured.
The names the service gives to its metrics are used in the service's Telemetry configuration to enable/disable the reporting of those metrics. See Core Data's Writable.Telemetry at Core Data Configuration as example of the names used for the service metrics that Core Data is currently collecting.
The following metric types are available to be used by the EdgeX services:
- Counter: Integer value that is incremented or decremented. Metric field name is
counter-count - Gauge: Integer value that is set to a specific value. Metric field name is
gauge-value - GaugeFloat64: Float value that is set to a specific value. Metric field name is
gaugeFloat64-value - Timer: Float value that is set to the amount of time an action takes. Metric field names are
timer-count,timer-min,timer-max,timer-mean,timer-stddevandtimer-variance
Service metrics which are enabled for reporting are published to the EdgeX MessageBug every configured interval using the configured Telemetry base topic. See Writable.Telemetry at Common Configuration for details on these configuration items. The service name and the metric name are added to the configured base topic. This allows subscribers to subscribe only for specific metrics or metrics from specific services. Each metric is published (reported) independently using the Metric DTO (Data Transfer Object) define in go-mod-core-contracts.
The aggregation of these service metrics is left to adopters to implement as best suits their deployment(s).
This can be accomplished with a custom application service that sets the function pipeline Target Type to the dtos.Metric type. Then create a custom pipeline function which aggregates the metrics and provides them to the telemetry dashboard service of choice via push (export) or pull (custom GET endpoint). See App Services here for more details on Target Type.
Example - DTO from Core Data in JSON format for the EventsPersisted metric as publish to the EdgeX MessageBus
{
"apiVersion": "v2",
"name": "EventsPersisted",
"fields": [
{
"name": "counter-count",
"value": 276
}
],
"tags": [
{
"name": "service",
"value": "core-data"
}
],
"timestamp": 1650301898926166900
}
Note
The service name is added to the tags for every metric reported from each service. Additional tags may be added via the service's Telemetry configuration. See the Writable.Telemetry at Common Configuration for more details. A service may also add metric specific tags via code when it collects the individual metrics.