Using the Virtual Device Service
Overview
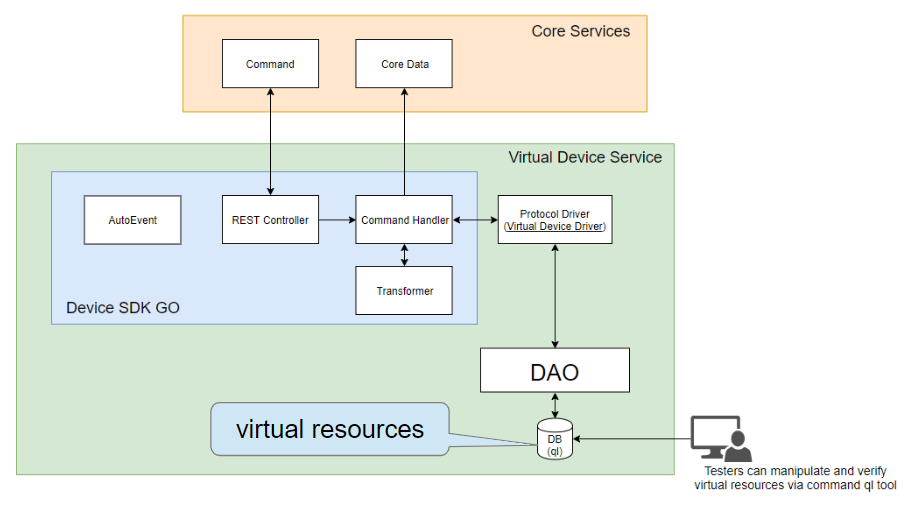
The Virtual Device Service GO can simulate different kinds of devices to generate Events and Readings to the Core Data Micro Service. Furthermore, users can send commands and get responses through the Command and Control Micro Service. The Virtual Device Service allows you to execute functional or performance tests without any real devices. This version of the Virtual Device Service is implemented based on Device SDK GO, and uses ql (an embedded SQL database engine) to simulate virtual resources.
Introduction
For information on the virtual device service see virtual device under the Microservices tab.
Working with the Virtual Device Service
Running the Virtual Device Service Container
The virtual device service depends on the EdgeX core services. By default, the virtual device service is part of the EdgeX community provided Docker Compose files. If you use one of the community provide Compose files, you can pull and run EdgeX inclusive of the virtual device service without having to make any changes.
Running the Virtual Device Service Natively (in development mode)
If you're going to download the source code and run the virtual device service in development mode, make sure that the EdgeX core service containers are up before starting the virtual device service. See how to work with EdgeX in a hybrid environment in order to run the virtual device service outside of containers. This same file will instruct you on how to get and run the virtual device service code.
GET command example
The virtual device service is configured to send simulated data to core data every few seconds (from 10-30 seconds depending on device - see the configuration file for AutoEvent details). You can excersice the GET request on the command service to see the generated value produced by any of the virtual device's simulated devices. Use the curl command below to exercise the virtual device service API (via core command service).
curl -X GET localhost:48082/api/v1/device/1bd5d4c3-9d43-42f2-8c4a-f32f5999edf7/command/e5d7c2b8-eab7-4da4-9d41-388da05979a4`
Warning
The example above assumes your core command service is available on localhost at the default service port of 48082. Also, you must replace your device ID and command ID in the example above with your virtual device service's identifiers. If you are not sure of the identifiers to use, query the command service for the full list of commands and devices at http://localhost:48082/api/v1/device.
The virtual device should respond (via the core command service) with event/reading JSON similar to that below.
{
"device": "Random-Integer-Device",
"origin": 1574325994604494491,
"readings": [
{
"origin": 1574325994572380549,
"device": "Random-Integer-Device",
"name": "Int8",
"value": "42"
}
],
"EncodedEvent": null
}
PUT command example - Assign a value to a resource
The virtual devices managed by the virtual device can also be actuated. The virtual device can be told to enable or disable random number generation. When disabled, the virtual device services can be told what value to respond with for all GET operations. When setting the fixed value, the value must be valid for the data type of the virtual device. For example, the minimum value of Int8 cannot be less than -128 and the maximum value cannot be greater than 127.
Below is example actuation of one of the virtual devices. In this example, it sets the fixed GET return value to 123 and turns off random generation.
curl -X PUT -d '{"Int8": "123", "EnableRandomization_Int8": "false"}' localhost:48082/api/v1/device/1bd5d4c3-9d43-42f2-8c4a-f32f5999edf7/command/e5d7c2b8-eab7-4da4-9d41-388da05979a4
Note
The value of the resource's EnableRandomization property is simultaneously updated to false when sending a put command to assign a specified value to the resource. Therefore, the need to set EnableRandomization_Int8 to false is not actually required in the call above
Return the virtual device to randomly generating numbers with another PUT call.
curl -X PUT -d '{"EnableRandomization_Int8": "true"}' 48082/api/v1/device/1bd5d4c3-9d43-42f2-8c4a-f32f5999edf7/command/e5d7c2b8-eab7-4da4-9d41-388da05979a4
Manipulate Virtual Resources Using the command ql Tool
The virtual device service utilizes the ql database under he covers to store parameters for virtual device operations. The values a virtual device generates can be controlled by changing these parameters in the embedded database (versus calling on the API).
-
You will need a command line tool to interact with the ql database. Install command ql.
-
Depending on whether you are running the virtual device service in a Docker container or in development mode ("natively"), you will need access to the ql database directory (see the tabs below).
-
Execute ql commands to execute SQL commands to see the virtual device configuration in the database or change the values returned.
- Query all data:
ql -db /path-to-the-ql-db-folder/deviceVirtual.db -fld "select * from VIRTUAL_RESOURCE" -
Update Enable_Randomization:
ql -db /path-to-the-ql-db-folder/deviceVirtual.db "update VIRTUAL_RESOURCE set ENABLE_RANDOMIZATION=false where DEVICE_NAME="Random-Integer-Device" and DEVICE_RESOURCE_NAME="Int8" " -
Update Value:
ql -db /path-to-the-ql-db-folder/deviceVirtual.db "update VIRTUAL_RESOURCE set VALUE="26" where DEVICE_NAME="Random-Integer-Device" and DEVICE_RESOURCE_NAME="Int8" "
Note
When running the virtual device service in a container, make sure to run these commands as
rootusing sudo. - Query all data:
If the virtual device service runs in a Docker container, it must mount the directory (/db) that contains the ql database in the container. For example:
device-virtual:
image: edgexfoundry/docker-device-virtual-go:1.2.1
ports:
- "127.0.0.1:49990:49990"
container_name: edgex-device-virtual
hostname: edgex-device-virtual
networks:
- edgex-network
environment:
<<: *common-variables
Service_Host: edgex-device-virtual
depends_on:
- consul
# - logging # uncomment if re-enabled remote logging
- data
- metadata
volumes:
- /mnt/hgfs/EdgeX/DeviceVirtualDB:/db # Mount ql database directory
If the virtual device service runs in development mode, the ql database is under the device-virtual-go/cmd/db directory.
Reference
Architectural Diagram
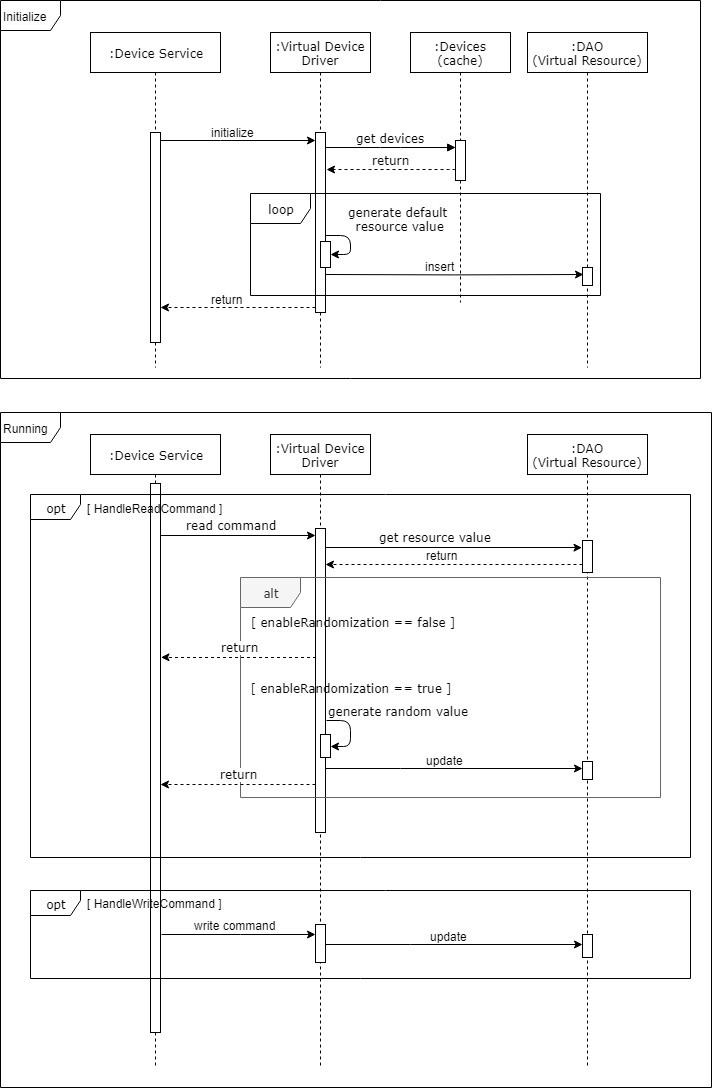
Sequence Diagram
Virtual Resource Table Schema
| Column | Type |
|---|---|
| DEVICE_NAME | STRING |
| COMMAND_NAME | STRING |
| DEVICE_RESOURCE_NAME | STRING |
| ENABLE_RANDOMIZATION | BOOL |
| DATA_TYPE | STRING |
| VALUE | STRING |