MQTT
EdgeX - Ireland Release
Overview
In this example, we use a script to simulate a custom-defined MQTT device, instead of a real device. This provides a straight-forward way to test the device-mqtt features using an MQTT-broker.
Prepare the Custom Device Configuration
In this section, we create folders that contain files required for deployment of a customized device configuration to work with the existing device service:
- custom-config
|- profiles
|- my.custom.device.profile.yml
|- devices
|- my.custom.device.config.toml
Device Profile
The DeviceProfile defines the device's values and operation method, which can be Read or Write.
Create a device profile, named my.custom.device.profile.yml, with the
following content:
name: "my-custom-device-profile"
manufacturer: "iot"
model: "MQTT-DEVICE"
description: "Test device profile"
labels:
- "mqtt"
- "test"
deviceResources:
-
name: randnum
isHidden: true
description: "device random number"
properties:
valueType: "Float32"
readWrite: "R"
-
name: ping
isHidden: true
description: "device awake"
properties:
valueType: "String"
readWrite: "R"
-
name: message
isHidden: false
description: "device message"
properties:
valueType: "String"
readWrite: "RW"
deviceCommands:
-
name: values
readWrite: "R"
isHidden: false
resourceOperations:
- { deviceResource: "randnum" }
- { deviceResource: "ping" }
- { deviceResource: "message" }
Device Configuration
Use this configuration file to define devices and schedule jobs. device-mqtt generates a relative instance on start-up.
Create the device configuration file, named my.custom.device.config.toml, as shown below:
# Pre-define Devices
[[DeviceList]]
Name = "my-custom-device"
ProfileName = "my-custom-device-profile"
Description = "MQTT device is created for test purpose"
Labels = [ "MQTT", "test" ]
[DeviceList.Protocols]
[DeviceList.Protocols.mqtt]
CommandTopic = "CommandTopic"
[[DeviceList.AutoEvents]]
Interval = "30s"
OnChange = false
SourceName = "message"
CommandTopicis used to publish the GET or SET command request
Prepare docker-compose file
- Clone edgex-compose
$ git clone git@github.com:edgexfoundry/edgex-compose.git $ git checkout ireland - Generate the docker-compose.yml file (notice this includes mqtt-broker)
Check the generated file
$ cd edgex-compose/compose-builder $ make gen ds-mqtt mqtt-broker no-secty ui$ ls | grep 'docker-compose.yml' docker-compose.yml
Mount the custom-config
Open the docker-compose.yml file and then add volumes path and environment as shown below:
- Replace the
/path/to/custom-configin the example with the correct path
device-mqtt:
...
environment:
...
DEVICE_DEVICESDIR: /custom-config/devices
DEVICE_PROFILESDIR: /custom-config/profiles
volumes:
...
- /path/to/custom-config:/custom-config
Start EdgeX Foundry on Docker
Deploy EdgeX using the following commands:
$ cd edgex-compose/compose-builder
$ docker-compose pull
$ docker-compose up -d
Run an MQTT Device Simulator
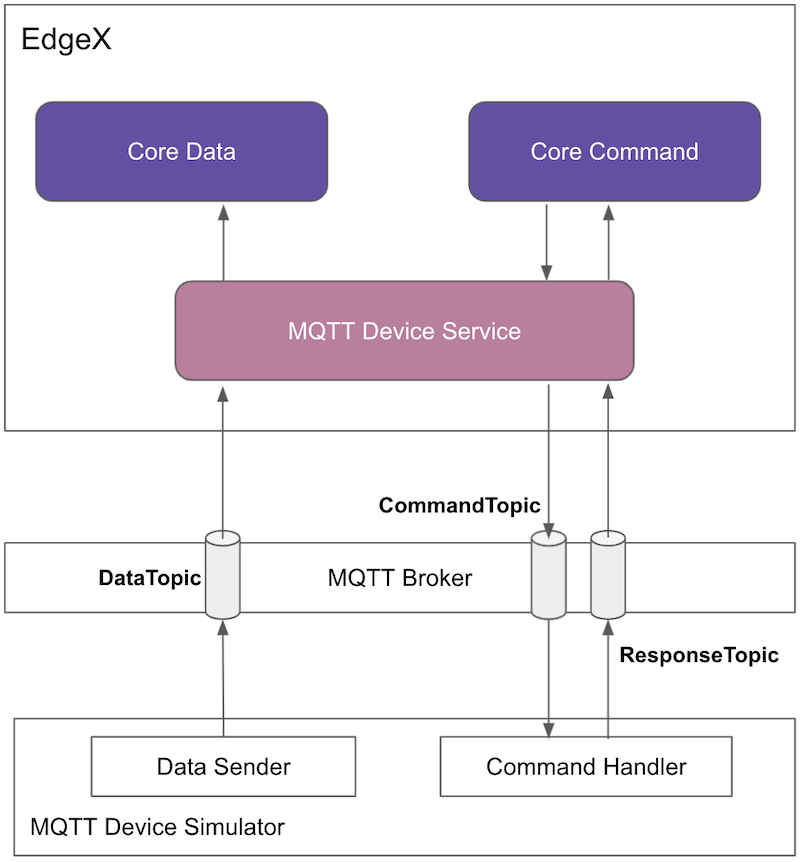
Using the detailed script below as a simulator, there are three behaviors:
-
Publish random number data every 15 seconds.
The simulator publishes the data to the MQTT broker with topic
DataTopicand the message is similar to the following:{"name":"my-custom-device", "cmd":"randnum", "method":"get", "randnum":4161.3549} -
Receive the reading request, then return the response.
- The simulator receives the request from the MQTT broker, the topic is
CommandTopicand the message is similar to the following:{"cmd":"randnum", "method":"get", "uuid":"293d7a00-66e1-4374-ace0-07520103c95f"} - The simulator returns the response to the MQTT broker, the topic is
ResponseTopicand the message is similar to the following:{"cmd":"randnum", "method":"get", "uuid":"293d7a00-66e1-4374-ace0-07520103c95f", "randnum":42.0} -
Receive the set request, then change the device value.
-
The simulator receives the request from the MQTT broker, the topic is
CommandTopicand the message is similar to the following:{"cmd":"message", "method":"set", "uuid":"293d7a00-66e1-4374-ace0-07520103c95f", "message":"test message..."} - The simulator changes the device value and returns the response to the MQTT broker, the topic is
ResponseTopicand the message is similar to the following:{"cmd":"message", "method":"set", "uuid":"293d7a00-66e1-4374-ace0-07520103c95f"}
- The simulator receives the request from the MQTT broker, the topic is
To implement the simulated custom-defined MQTT device, create a javascript, named mock-device.js, with the
following content:
function getRandomFloat(min, max) {
return Math.random() * (max - min) + min;
}
const deviceName = "my-custom-device";
let message = "test-message";
// DataSender sends async value to MQTT broker every 15 seconds
schedule('*/15 * * * * *', ()=>{
let body = {
"name": deviceName,
"cmd": "randnum",
"randnum": getRandomFloat(25,29).toFixed(1)
};
publish( 'DataTopic', JSON.stringify(body));
});
// CommandHandler receives commands and sends response to MQTT broker
// 1. Receive the reading request, then return the response
// 2. Receive the set request, then change the device value
subscribe( "CommandTopic" , (topic, val) => {
var data = val;
if (data.method == "set") {
message = data[data.cmd]
}else{
switch(data.cmd) {
case "ping":
data.ping = "pong";
break;
case "message":
data.message = message;
break;
case "randnum":
data.randnum = 12.123;
break;
}
}
publish( "ResponseTopic", JSON.stringify(data));
});
To run the device simulator, enter the commands shown below with the following changes:
- Replace the
/path/to/mqtt-scriptsin the example mv command with the correct path$ mv mock-device.js /path/to/mqtt-scripts $ docker run -d --restart=always --name=mqtt-scripts \ -v /path/to/mqtt-scripts:/scripts \ dersimn/mqtt-scripts --url mqtt://172.17.0.1 --dir /scriptsThe address
172.17.0.1is point to the host of MQTT broker via the docker bridge network.
Execute Commands
Now we're ready to run some commands.
Find Executable Commands
Use the following query to find executable commands:
$ curl http://localhost:59882/api/v2/device/all | json_pp
{
"deviceCoreCommands" : [
{
"profileName" : "my-custom-device-profile",
"deviceName" : "my-custom-device",
"coreCommands" : [
{
"url" : "http://edgex-core-command:59882",
"parameters" : [
{
"resourceName" : "randnum",
"valueType" : "Float32"
},
{
"resourceName" : "ping",
"valueType" : "String"
},
{
"resourceName" : "message",
"valueType" : "String"
}
],
"get" : true,
"name" : "values",
"path" : "/api/v2/device/name/my-custom-device/values"
},
{
"url" : "http://edgex-core-command:59882",
"parameters" : [
{
"valueType" : "String",
"resourceName" : "message"
}
],
"get" : true,
"set" : true,
"path" : "/api/v2/device/name/my-custom-device/message",
"name" : "message"
}
]
}
],
"apiVersion" : "v2",
"statusCode" : 200
}
Execute SET Command
Execute a SET command according to the url and parameterNames, replacing [host] with the server IP when running the SET command.
$ curl http://localhost:59882/api/v2/device/name/my-custom-device/message \
-H "Content-Type:application/json" -X PUT \
-d '{"message":"Hello!"}'
Execute GET Command
Execute a GET command as follows:
$ curl http://localhost:59882/api/v2/device/name/my-custom-device/message | json_pp
{
"event" : {
"origin" : 1624417689920618131,
"readings" : [
{
"resourceName" : "message",
"binaryValue" : null,
"profileName" : "my-custom-device-profile",
"deviceName" : "my-custom-device",
"id" : "a3bb78c5-e76f-49a2-ad9d-b220a86c3e36",
"value" : "Hello!",
"valueType" : "String",
"origin" : 1624417689920615828,
"mediaType" : ""
}
],
"sourceName" : "message",
"deviceName" : "my-custom-device",
"apiVersion" : "v2",
"profileName" : "my-custom-device-profile",
"id" : "e0b29735-8b39-44d1-8f68-4d7252e14cc7"
},
"apiVersion" : "v2",
"statusCode" : 200
}
Schedule Job
The schedule job is defined in the [[DeviceList.AutoEvents]] section of the device configuration file:
[[DeviceList.AutoEvents]]
Interval = "30s"
OnChange = false
SourceName = "message"
After the service starts, query core-data's reading API. The results show that the service auto-executes the command every 30 secs, as shown below:
$ curl http://localhost:59880/api/v2/reading/resourceName/message | json_pp
{
"statusCode" : 200,
"readings" : [
{
"value" : "test-message",
"id" : "e91b8ca6-c5c4-4509-bb61-bd4b09fe835c",
"mediaType" : "",
"binaryValue" : null,
"resourceName" : "message",
"origin" : 1624418361324331392,
"profileName" : "my-custom-device-profile",
"deviceName" : "my-custom-device",
"valueType" : "String"
},
{
"mediaType" : "",
"binaryValue" : null,
"resourceName" : "message",
"value" : "test-message",
"id" : "1da58cb7-2bf4-47f0-bbb8-9519797149a2",
"deviceName" : "my-custom-device",
"valueType" : "String",
"profileName" : "my-custom-device-profile",
"origin" : 1624418330822988843
},
...
],
"apiVersion" : "v2"
}
Async Device Reading
The device-mqtt subscribes to a DataTopic, which is wait for the real device to send value to MQTT broker, then device-mqtt
parses the value and forward to the northbound.
The data format contains the following values:
- name = device name
- cmd = deviceResource name
- method = get or set
- cmd = device reading
The following results show that the mock device sent the reading every 15 secs:
$ curl http://localhost:59880/api/v2/reading/resourceName/randnum | json_pp
{
"readings" : [
{
"origin" : 1624418475007110946,
"valueType" : "Float32",
"deviceName" : "my-custom-device",
"id" : "9b3d337e-8a8a-4a6c-8018-b4908b57abb8",
"binaryValue" : null,
"resourceName" : "randnum",
"profileName" : "my-custom-device-profile",
"mediaType" : "",
"value" : "2.630000e+01"
},
{
"deviceName" : "my-custom-device",
"valueType" : "Float32",
"id" : "06918cbb-ada0-4752-8877-0ef8488620f6",
"origin" : 1624418460007833720,
"mediaType" : "",
"profileName" : "my-custom-device-profile",
"value" : "2.570000e+01",
"resourceName" : "randnum",
"binaryValue" : null
},
...
],
"statusCode" : 200,
"apiVersion" : "v2"
}
MQTT Device Service Configuration
MQTT Device Service has the following configurations to implement the MQTT protocol.
| Configuration | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MQTTBrokerInfo.Schema | tcp | The URL schema |
| MQTTBrokerInfo.Host | 0.0.0.0 | The URL host |
| MQTTBrokerInfo.Port | 1883 | The URL port |
| MQTTBrokerInfo.Qos | 0 | Quality of Service 0 (At most once), 1 (At least once) or 2 (Exactly once) |
| MQTTBrokerInfo.KeepAlive | 3600 | Seconds between client ping when no active data flowing to avoid client being disconnected. Must be greater then 2 |
| MQTTBrokerInfo.ClientId | device-mqtt | ClientId to connect to the broker with |
| MQTTBrokerInfo.CredentialsRetryTime | 120 | The retry times to get the credential |
| MQTTBrokerInfo.CredentialsRetryWait | 1 | The wait time(seconds) when retry to get the credential |
| MQTTBrokerInfo.ConnEstablishingRetry | 10 | The retry times to establish the MQTT connection |
| MQTTBrokerInfo.ConnRetryWaitTime | 5 | The wait time(seconds) when retry to establish the MQTT connection |
| MQTTBrokerInfo.AuthMode | none | Indicates what to use when connecting to the broker. Must be one of "none" , "usernamepassword" |
| MQTTBrokerInfo.CredentialsPath | credentials | Name of the path in secret provider to retrieve your secrets. Must be non-blank. |
| MQTTBrokerInfo.IncomingTopic | DataTopic | IncomingTopic is used to receive the async value |
| MQTTBrokerInfo.responseTopic | ResponseTopic | ResponseTopic is used to receive the command response from the device |
| MQTTBrokerInfo.Writable.ResponseFetchInterval | 500 | ResponseFetchInterval specifies the retry interval(milliseconds) to fetch the command response from the MQTT broker |
The user can override these configurations by environment variable to meet their requirement, for example:
# docker-compose.yml
device-mqtt:
...
environment:
...
DEVICE_DEVICESDIR: /custom-config/devices
DEVICE_PROFILESDIR: /custom-config/profiles